 Open wechat
Open wechat
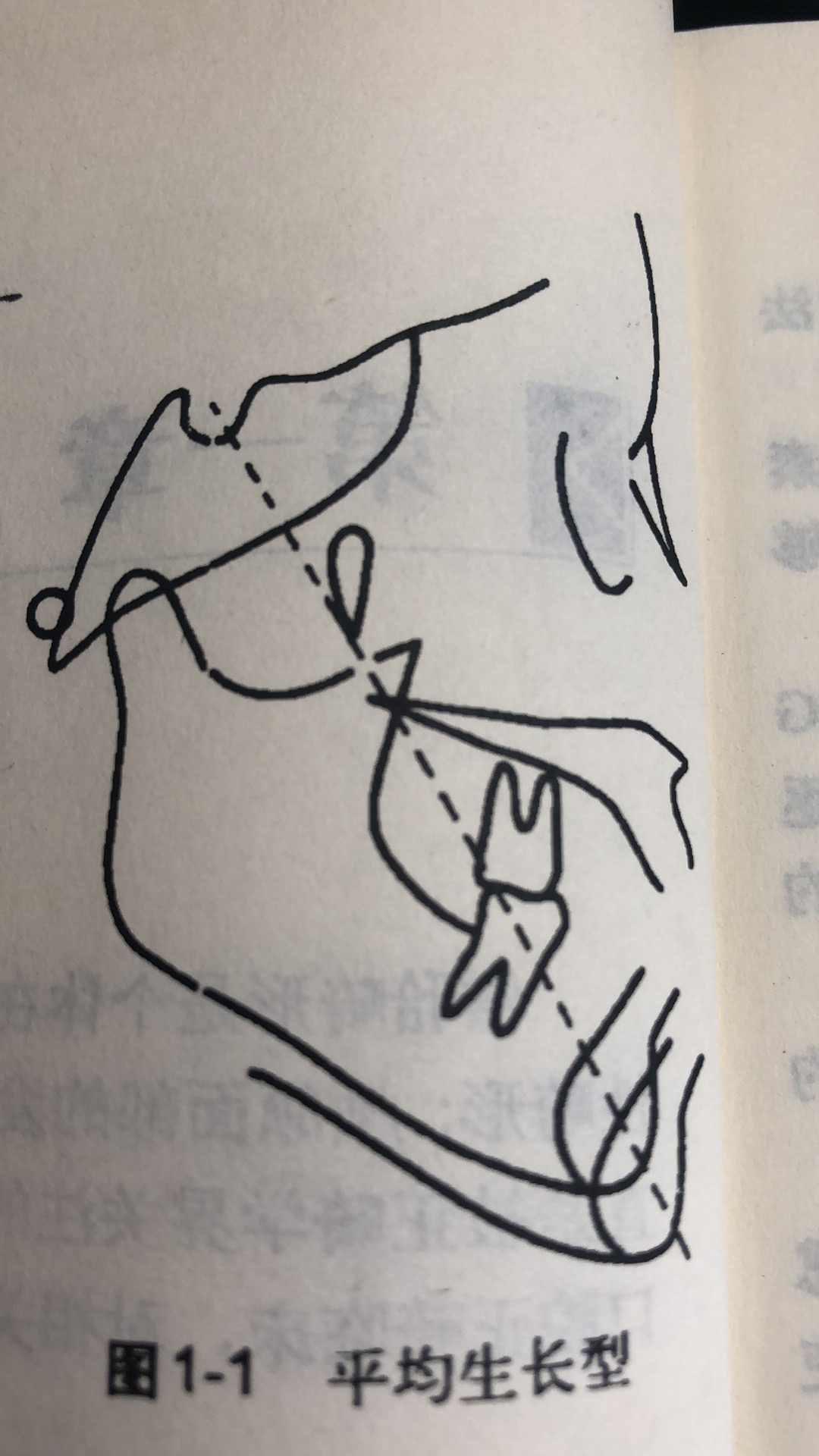
(1) Average growth type
The chin point of the mandible grows forward and downward along the Y axis. The descending of the articular fossa and the vertical growth of the superior alveolar process are balanced and coordinated with the vertical downward growth and movement of the maxillary body and the superior alveolar process and the upward growth of the inferior alveolar process.
(2) horizontal growth type
The growth of this type of mandible shows a closed rotation in a counterclockwise direction, and its buccal apex obviously moves forward and upward during the growth process. The reason is the vertical growth of maxillary and upper and lower alveolar, the vertical growth of small thousand joint fossa and ankle process, that is, the disharmony between the front and the back. Most of them are short face type, with a trend of deep covering.
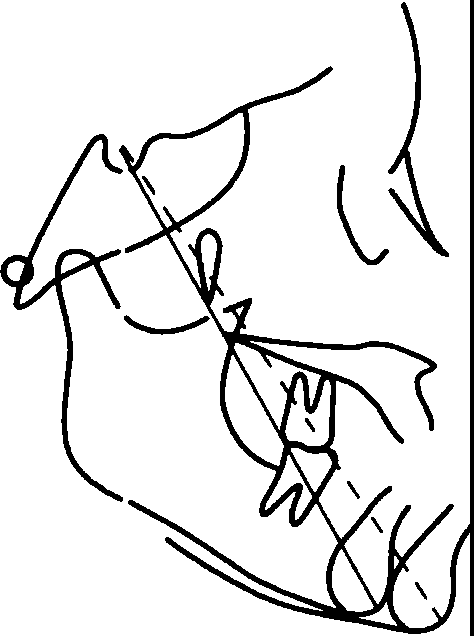
Horizontal growth type
(3) vertical growth type
The vertically growing mandible rotates clockwise, and the buccal apex moves backward and downward obviously. The reason is the vertical growth of the upper jaw and upper and lower alveolar, and the vertical growth of the joint fossa and ankle process, that is, the growth in the front and the growth in the back. Most of them are long face type and tend to be open and reserved. Generally, the mandibular plane angle is too large, that is, the so-called "high angle cases" which are more common in clinic.
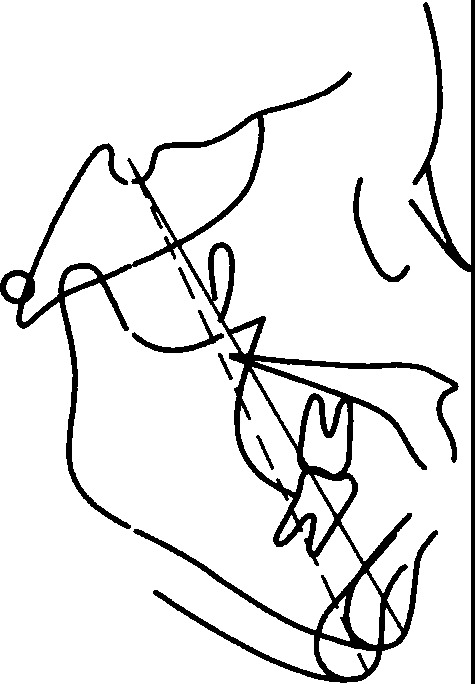

Vertical growth type
4 growth variation
Growth variation is one of the laws of nature and the result of the joint action of genetic and environmental factors. The normal body of a population we discussed changes to a certain extent in the process of growth and development, which is called growth variation. The most important clinical significance of growth variation is to determine the "normal variation range", which is also a difficulty in clinical work. Some indicators that can reflect the general growth and development of the body, such as height, weight and other standard growth curves, are often used for comparative analysis to judge whether the variation of an individual is within the normal range.
5 growth period
In the process of normal craniomaxillofacial growth and development, it does not increase with age at the same rate, but grows rapidly in one period and slows down in another period. The period corresponding to this phenomenon is called growth period.

