 Open wechat
Open wechatAt present, all ceramic teeth have become the first choice of dental restorative materials. In addition to excellent mechanical properties, they also have excellent biocompatibility, which will not cause gum speech and will not block X-ray. Their types can be simply divided into three types, namely zirconia all ceramic teeth, cast ceramic teeth and alumina all ceramic teeth.
Among the three materials, zirconia is the strongest one, and its fracture toughness ratio is twoorthree times that of alumina, so it is not easy to crack; Secondly, compared with other materials, zirconia is more beautiful. It can also be "confused with the real" by means of coloring and porcelain decoration, so it has become the most popular all ceramic dental material.
refine on
However, people always have to go higher, and the dental restoration industry is also pursuing repair materials with better performance. Although the performance of zirconia can basically meet people's daily needs, it still has some unsatisfactory places. For example, although zirconia is beautiful compared with other restoration materials, it will still have poor aesthetic effect due to poor light transmission performance when used as crown and bridge restoration materials. Therefore, in clinical application, decorative porcelain will be added to the surface to cover it up. However, the strength of decorative porcelain is different from that of zirconia, which leads to porcelain collapse, which has become one of the most common reasons for the failure of zirconia crown restoration.
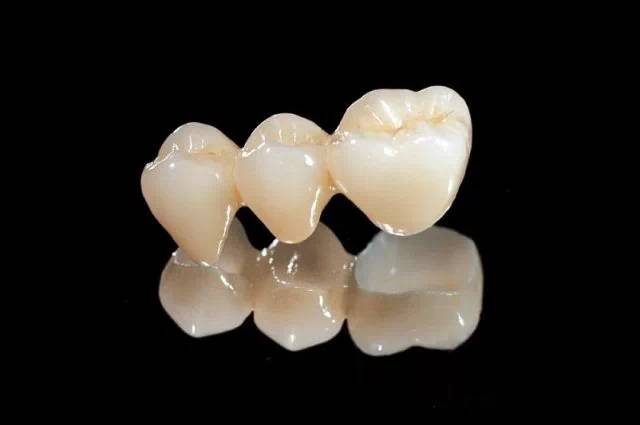
Full zirconium crown bridge
As the saying goes, it's better to rely on yourself than on others. If zirconia ceramics themselves can be more handsome, doesn't it need external forces? Therefore, with the further development of material technology, the industry began to study how to make more transparent ultra transparent zirconia materials.
Factors affecting the semi permeability of zirconia
As the name suggests, ultra transparent zirconia is a new material that combines the inherent corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and insulation properties of ceramic materials, and has similar optical properties as glass ceramics. The differences between it and ordinary zirconia ceramics mainly focus on the following points:
01. grain diameter
The size of grains affects the transmittance. When the grain diameter is closer to the visible light wavelength of 380~780nm, the maximum light absorption will be produced, resulting in low transmittance; When the grain size is smaller than the wavelength of incident light, the light transmittance is high. The particles with small and uniform diameter can realize dense arrangement, so as to increase the density of the material, reduce the number of pores and reduce the pore diameter, which has a decisive impact on the improvement of the semi permeability of the material.
It has been found that zirconia ceramics with a grain size of 82nm and a thickness of 1.3mm have good semi permeability; When the thickness increases to 1.5 and 2.0mm, in order to maintain the same semi permeability, the grain size needs to be reduced to 77 and 70nm respectively. When the grain size is reduced to submicron or nano scale, opaque polycrystalline ceramics can be made translucent. However, it should be noted that the increase or decrease of grain size will affect the strength of zirconia ceramics.
02. Type and amount of added phase
Adding phase can change the relative density and particle size of zirconia ceramics, increase the composition of ceramic microstructure, change the optical uniformity of zirconia ceramics, and affect the semi permeability of ceramics. 3Y tetragonal zirconia polycrystals with yttria as stabilizer have good strength and toughness, excellent stability and wear resistance. Typical 3Y TZP is composed of 5.18% yttrium (3mol%) and >90% tetragonal zirconia. With the increase of yttrium content, the cubic phase and semi permeability of zirconia increase.
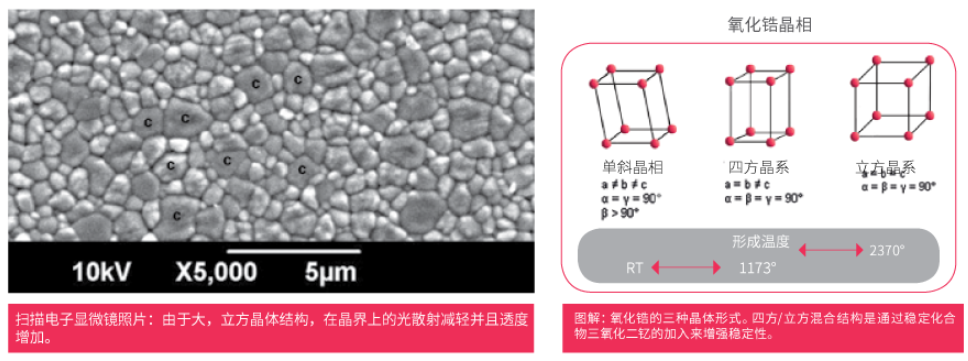
3M introduced a translucent zirconia powder containing 7.10wt% yttrium in 2014, with an average grain size of 150nm, containing 75% tetragonal zirconia and 25% cubic zirconia. Increasing the number of cubic phase and decreasing the grain size can make the experimental material more transparent. TOSOH company in Japan also prepared translucent zirconia zpexsmile in the same way. However, due to the reduction of phase transformation toughening, the bending strength and fracture toughness of partially stabilized tetragonal zirconia decreased by 1/2 ~ 2/3. At present, zirconia products containing 8mol% yttrium have been used in clinic.
03. Proportion of Cubic Zirconia
Zirconia products on the market can be roughly divided into traditional zirconia, semi permeable zirconia, high permeable zirconia and ultra permeable zirconia according to the proportion of cubic zirconia. The higher the cubic phase proportion of zirconia, the more transparent the product is. This is because the refractive index of zirconia tetragonal phase is anisotropic in different crystal directions due to its birefringence; Light is reflected and refracted at the grain boundary, and the transmittance decreases, making the tetragonal phase less transparent. Isotropic cubic zirconia reduces light scattering from grain boundaries. By adding a higher proportion of yttrium oxide to stabilize the composition of zirconia, a higher proportion of cubic phase can be achieved.
04. air hole
Translucent ceramics should minimize pores during sintering. The general oxide ceramics obtained by solid-state sintering are usually not transparent even if their density is high. This is because the grains grow rapidly in the final stage of sintering, forming scattered closed pores. Zirconia crystal has a refractive index of 2.20, while air has only a refractive index of 1.00. When light passes through zirconia material, it will encounter pores and scatter. Pores will become the center of scattering.
Studies have shown that if the existence rate of pores is reduced from 0.85% to 0.25%, the light transmittance will increase by 33%. Optimizing the heat treatment process is an effective method to reduce pores. The lava zirconia all ceramic material of 3M company in the United States adopts the hot isostatic pressing sintering method to compact its internal structure, reduce the number of pores, reduce the light scattering, and obtain higher semi permeability. Harianawala and others believe that the pores of ultra permeable zirconia should be controlled at the nano level.
05. Sintering temperature
The less the pores are, the higher the transparency of the ceramics will be, and the higher the sintering temperature can reduce the number of pores. Therefore, with the increase of temperature, the ceramics will gradually densify, the grain diameter will increase, and the transmittance of the ceramics will also increase.
However, the sintering temperature still needs to be controlled within a reasonable range, because if the temperature continues to rise when the sintering is nearly completed, the grain boundary may produce secondary recrystallization, and impurities such as pores may be wrapped into the crystal, resulting in no increase in density. Small pores are easy to be incorporated into the low-pressure atmospheric pores, making the large pores larger and larger, and the sintered body expands. In addition to the sintering temperature, it is also necessary to control the heating rate to ensure that the whole material is evenly heated, control the growth rate and size of the crystal, and achieve the purpose of reducing pores. The final sintering temperature and holding time directly affect the sintering density and the light transmittance of the material.
Application of ultra transparent zirconia
However, the excellent semi permeability of ultra permeable zirconia is at the cost of weakening the strength. This is because the cubic phase is an isotropic but fragile phase. With the increase of cubic phase content, the phase transformation toughening ability decreases, and the strength and toughness decrease. The minimum fracture toughness required for dental ceramics to manufacture restorations with ≥ 4 units is 5mpam1/2, while 5y-psz ultra permeable zirconia with an average fracture toughness of 4.82mpam1/2 can only be used for restorations with ≤ 3 units. Therefore, ultra permeable zirconia is not recommended for posterior tooth restoration with ≥ 3 units. It is more suitable as a means of minimally invasive restoration of anterior teeth. For example, it can reduce the veneer thickness to 0.1~0.3mm and maintain good mechanical properties. Compared with glass ceramic restoration, it can retain more tooth tissue.

Ultra transparent zirconia
However, ultra permeable zirconia has high resistance to low-temperature aging, because yttrium oxide can form a stable solid solution with zirconia, thus preventing crystal transformation during zirconia cooling. At the same time, the cubic phase is a stable phase. In 5y-tzp ultra permeable zirconia, about 50% zirconia cubic phase is introduced into the high yttrium content (>5mol%), which makes 5y-tzp ceramics have high light transmittance and good aging resistance.
In application, medium permeable zirconia can be used to replace dentin, but it is not recommended to replace enamel, while ultra permeable zirconia can replace enamel without increasing the volume of prosthesis, which is suitable for ultra-thin prostheses such as partial crowns and veneers. In addition, the color range of ultra transparent zirconia ceramic discs is larger, which also reduces the demand for surface dyeing. In addition, if you want to get a more natural and realistic appearance, you can also combine the fine multi part polishing and the application of diamond polishing paste to improve the excellent surface gloss.

